SOLUTION DESIGN
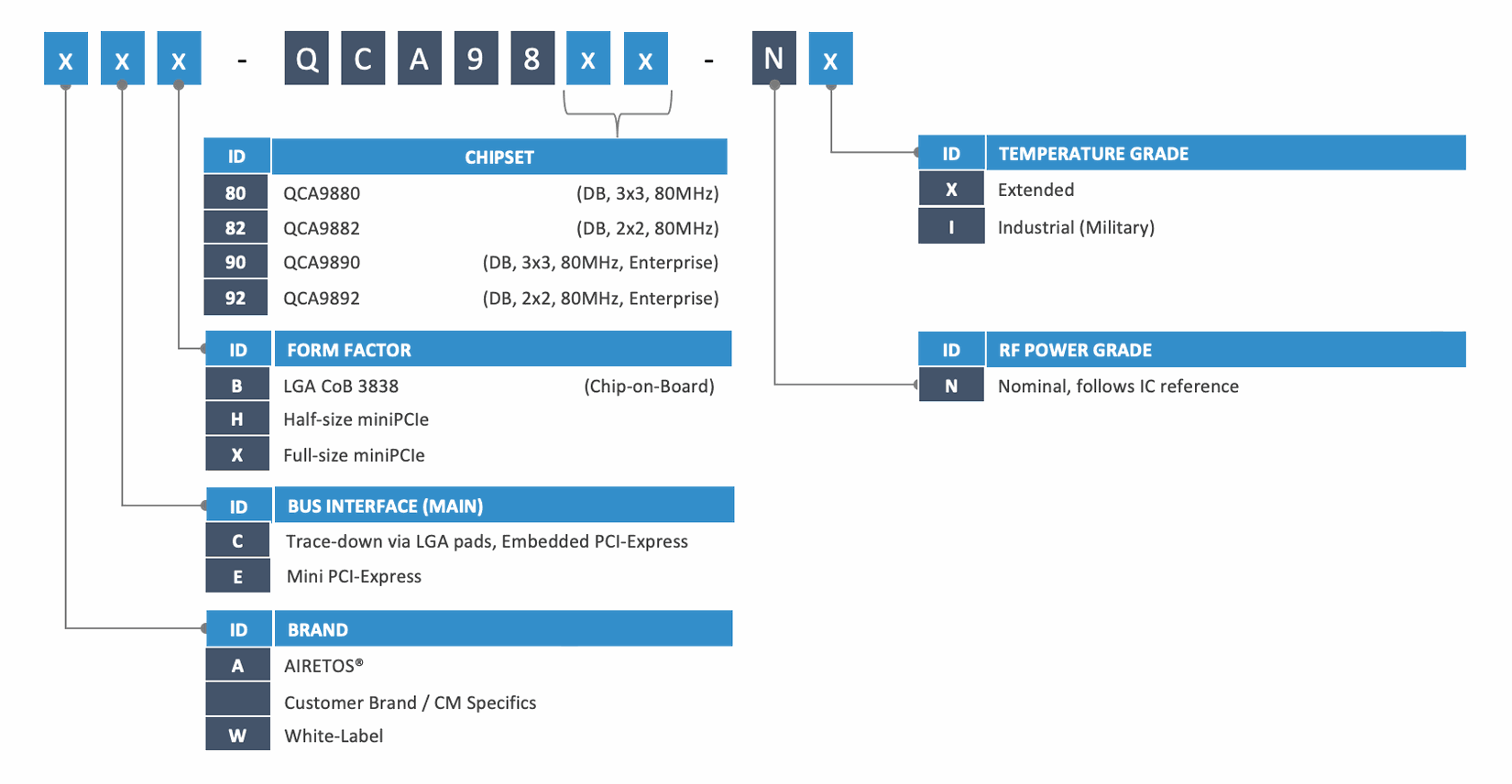
Chipset: Qualcomm QCA9880-BR4A, QCA9882-BR4A, QCA9890-BR4A, QCA9890-BR4B, QCA9892-BR4A or QCA9892-BR4B. Optional use of the respective QCA9886, QCA9887, QCA9888 or QCA9889.
Standard: IEEE 802.11ac Wi-Fi5, full backwards compatibility to previous standards
Industrial Reference: Based on Qualcomm Atheros reference design XB140 Enterprise Version 2
APPEARANCE
Communications Interface:
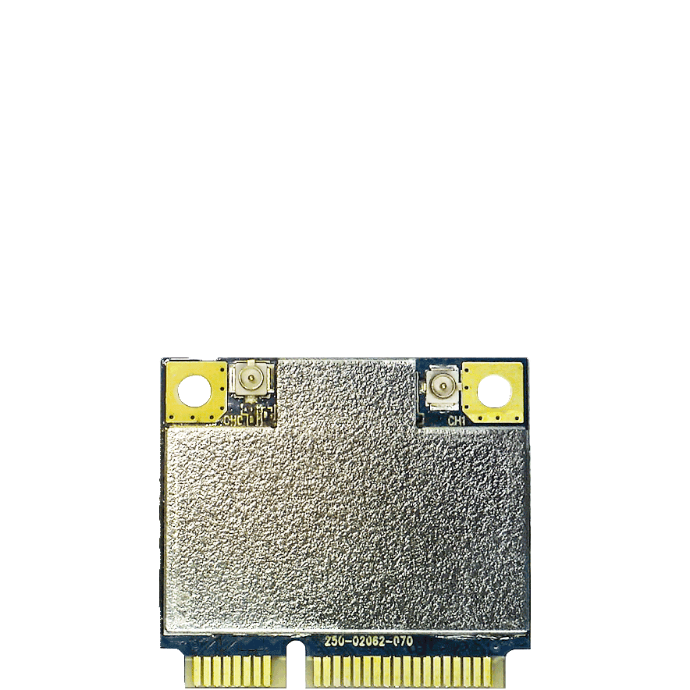
Pads: LGA-type solder pads or edge connector:
WLAN: via PCI Express Standard 2.0 host I/O
Form Factor:
For E98B: SMD, Chip-on-Board, Soldered, Stamp down, 71 each of peripheral Land Grid Array (LGA) type pins, 37.8 x 37.8 mm
Others: Slotted, Socketed
ANTENNA
Configuration:
WLAN: Three Streams (3 chains), 3x3, 3 Connectors, MIMO
Type:
For the E98B: PCB trace pads for routing signals to host or to a carrier board
Others: Up to three on-board MHF1 Connectors.
WIRELESS PARAMETERS
Frequency Band:
WLAN:
2.4 GHz ISM Bands 2.412-2.472 GHz, 2.484 GHz
4.9425-4.985 GHz (optional band support for Japan and safety markets) 5.15-5.25 GHz (FCC UNII-low band) for US/Canada, Japan and Europe 5.25-5.35 GHz (FCC UNII-middle band) for US/Canada and Europe 5.47-5.725 GHz for Europe
5.725-5.825 GHz (FCC UNII-high band) for US/Canada
Data Transfer Rates:
WLAN:
802.11ac: Up to 1300Mbps (dynamic)
802.11n: Up to 300Mbps (dynamic)
802.11a/g: Up to 54Mbps (dynamic)
802.11b: Up to 11Mbps (dynamic)
Media Access Control: CSMA/CA with ACK
Channel:
2.4GHz: 1-13 (14 only for Japan)
4.9GHz: 7×20MHz (20-80), 2×10MHz (10, 90), 10×5MHz (5-95)
5GHz: 36-48, 149-165
Channel Spacing: 5MHz, 10MHz and 20 MHz selectable
Spreading / Modulation:
WLAN:
802.11ac/g/n: OFDM (BPSK,QPSK,16-QAM,64-QAM), MRC, STBC, LDPC, ML Demodulation
802.11b: CCK (11, 5.5Mbps), DQPSK (2Mbps), BPSK (1Mbps)
RF Output Power:
WLAN:
802.11a: Typical 13 dBm at 54M / 16dBm at 6M +- 2dBm
802.11b: Typical 18dBm +/- 2 dBm
802.11g: Typical 13 dBm at 54M / 18dBm at 6M +- 2dBm
802.11n 5G HT20 : Typical 21 dBm at MCS0 / 16dBm at MCS7 +/- 2dBm 802.11n 5G HT40 : Typical 21 dBm at MCS0 / 16dBm at MCS7 +/- 2dBm 802.11n 2.4G HT20 : Typical 22 dBm at MCS0 / 16dBm at MCS7 +/- 2dBm 802.11n 2.4G HT40 : Typical 22 dBm at MCS0 / 16dBm at MCS7 +/- 2dBm 802.11ac 5G VHT20 : Typical 21 dBm at MCS0 / 15dBm at MCS8 +/- 2dBm 802.11ac 5G VHT40 : Typical 21 dBm at MCS0 / 15dBm at MCS8 +/- 2dBm 802.11ac 5G VHT80 : Typical 21 dBm at MCS0 / 14dBm at MCS8 +/- 2dBm
• DBm values reflect single RF chain output power performance.
• Three chain combined output power can be calculated as the single chain output power above plus 5dB (3Tx = 1Tx + 5dB).
RF Receive Sensitivity (Typical, 1x1 chain):
WLAN:
802.11a: 54M less than -70 dBm
802.11b: 11M less than -85 dBm
802.11g: 54M less than -70 dBm
802.11n 2.4G:
HT20 MCS7 less than -72 dBm
HT40 MCS7 less than -69 dBm
802.11a 4.9GHz:
54M less than -75 dBm
6M less than -85 dBm
802.11n 5G:
HT20 MCS7 less than -72 dBm
HT40 MCS7 less than -69 dBm
802.11ac 5G:
VHT20 MCS8 less than -68 dBm
VHT40 MCS8 less than -64 dBm
VHT40 MCS8 less than -61 dBm
Operating Range:
Open Space: ~300 m; Indoor: :~100 m
(Coverage vary according to environment, antenna and topography)
Wireless Security:
WEP 64-bit and 128-bit encryption
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
MODALITIES
Infrastructure, AP/STA, Client, Bridge, Mixed-mode, P2P/Ad-hoc
SAFETY & REGULATORY
Compliant with FCC, IC ISED, EU CE and more.
Compliant with RoHS3.
PROTOCOLS
IEEE WLAN Network:
IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac (Wi-Fi5),
IEEE 802.11d, 802.11e, 802.11h, 802.11j and 802.11i
Other Standards:
Industry Standards:
HOST SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
Operating System: Android/Linux Closed Source, Android/Linux Open Source, Qualcomm Embedded Platform, Windows, MacOS
** 50+ MB memory (RAM) is recommended for best performance.
ENVIRONMENTAL
Operating Temperature: -40 to +85 Celsius (depending on MPN)
Storage Temperature: -40 to +90 Celsius
Operating Humidity: 10% to 90% non-condensing
Storage Humidity: 5% to 90% non-condensing
ELECTRICAL
Power Consumption:
PROTOCOL RATE: 3x3 CTx 3x3 CRx
HT 40*: 1151.27 mA max 563.64 mA max
• Electronic current values in milliampere. Readings retrieved under stable, typical current and voltage.
• Power consumption ratings are statistical maximums in test system setups which are placed in continuous operating modes.
• Real-life application system power budgets are dependent on traffic mix, environment, topology and domain configuration.
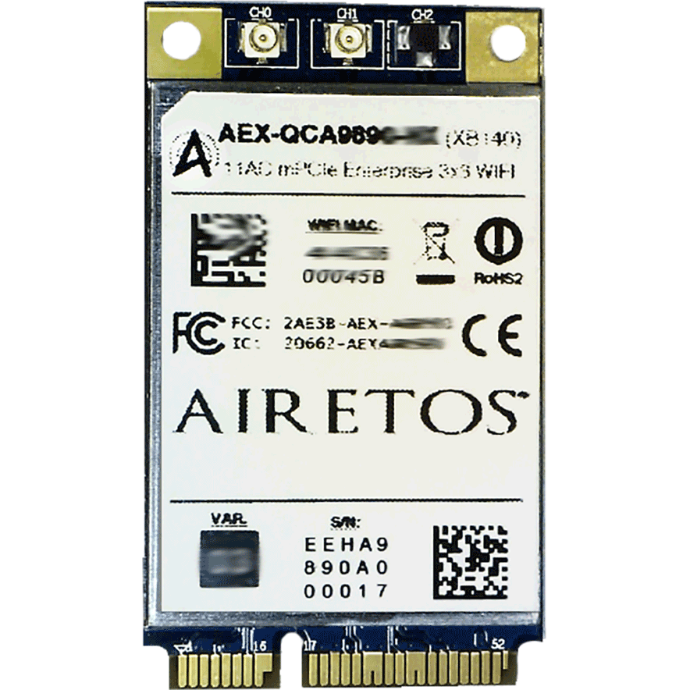







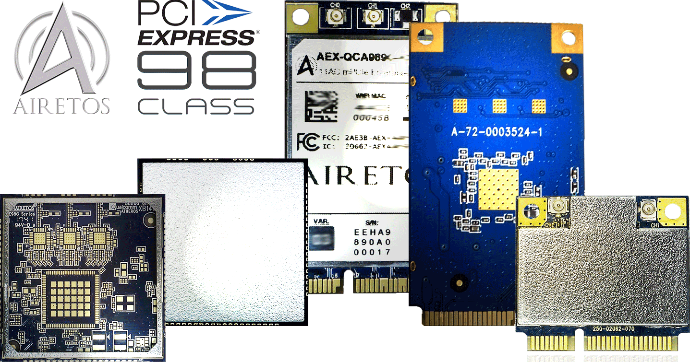













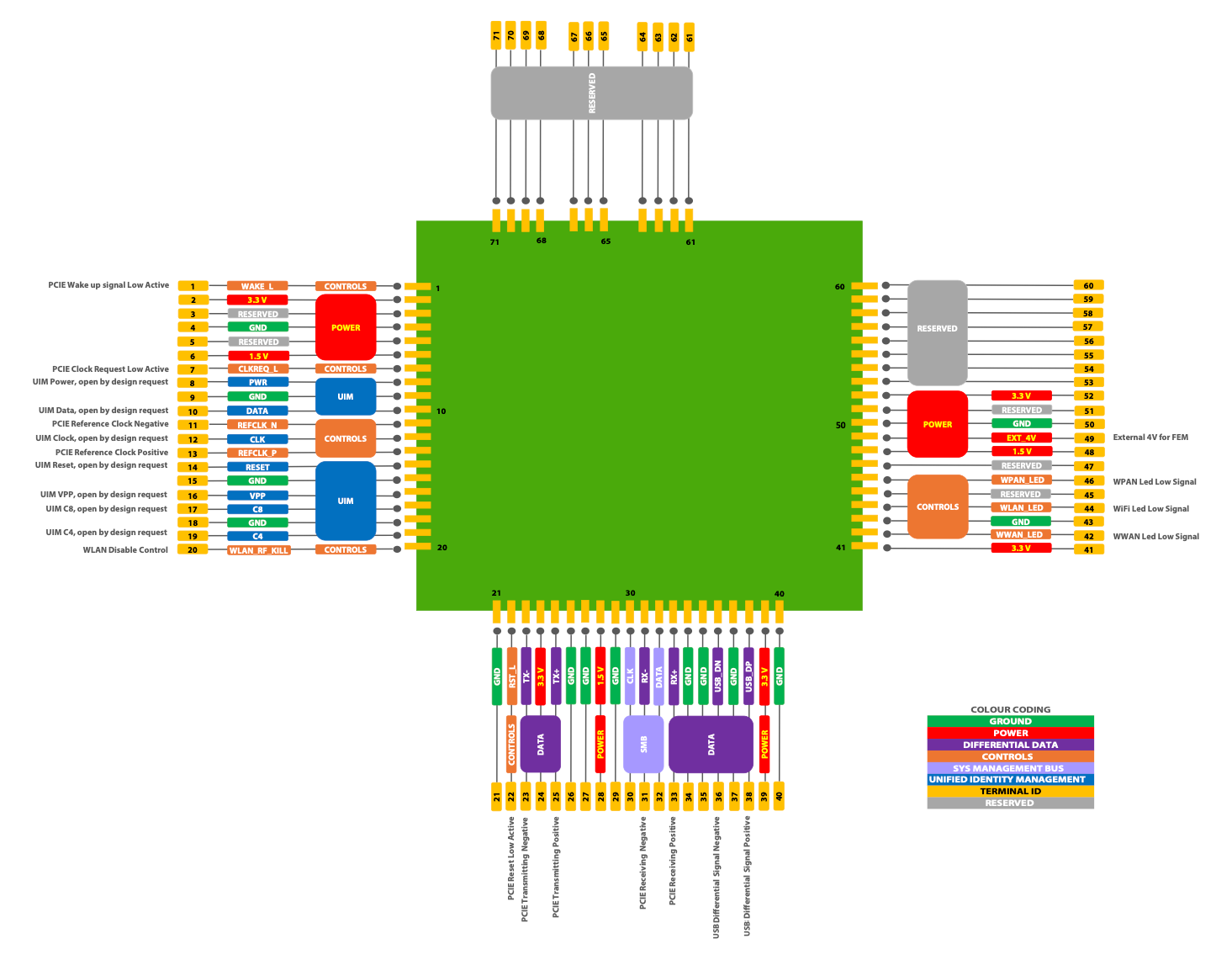
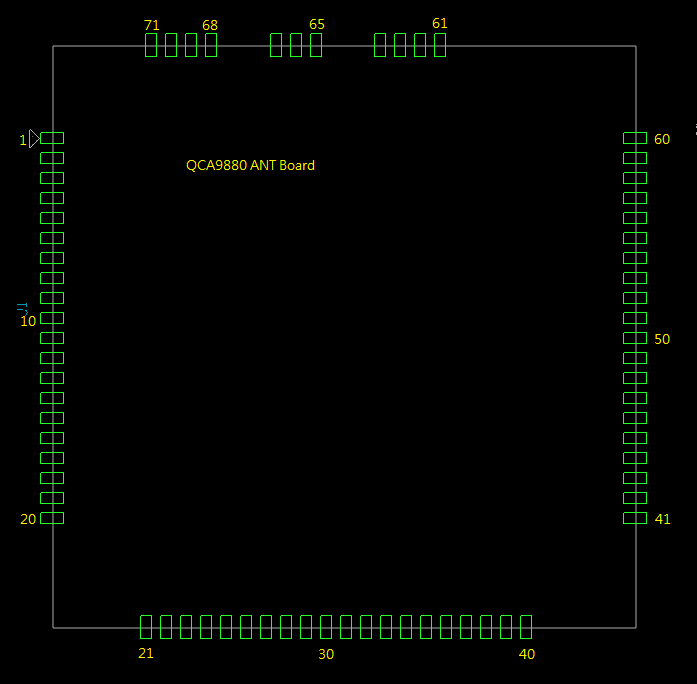
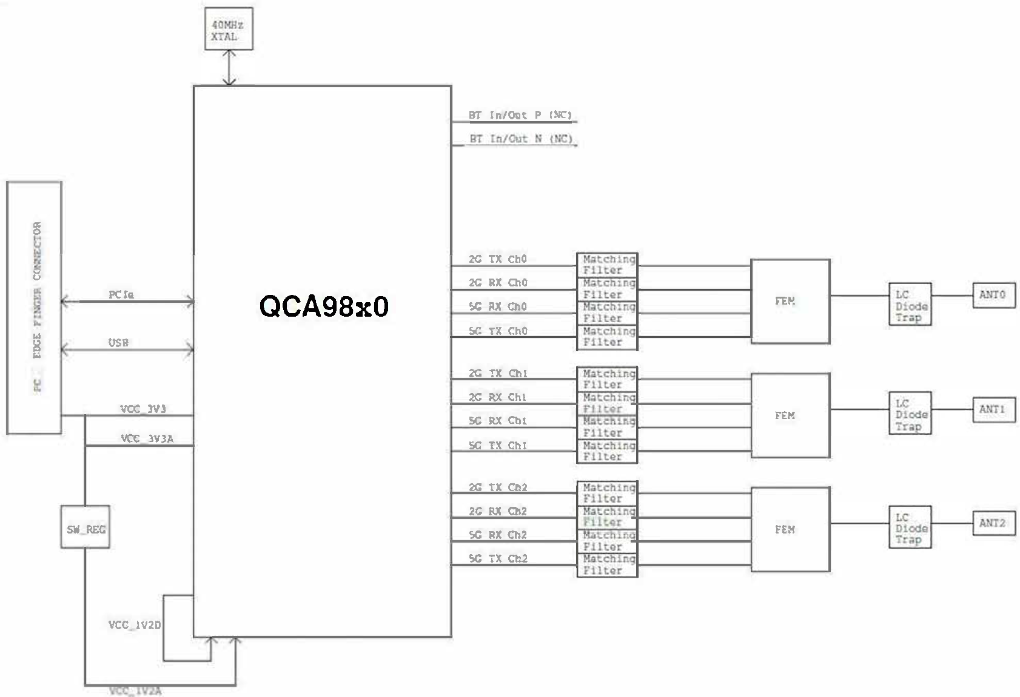 ** showing 3x3 E98 Block Diagram cconfiguration.
** showing 3x3 E98 Block Diagram cconfiguration.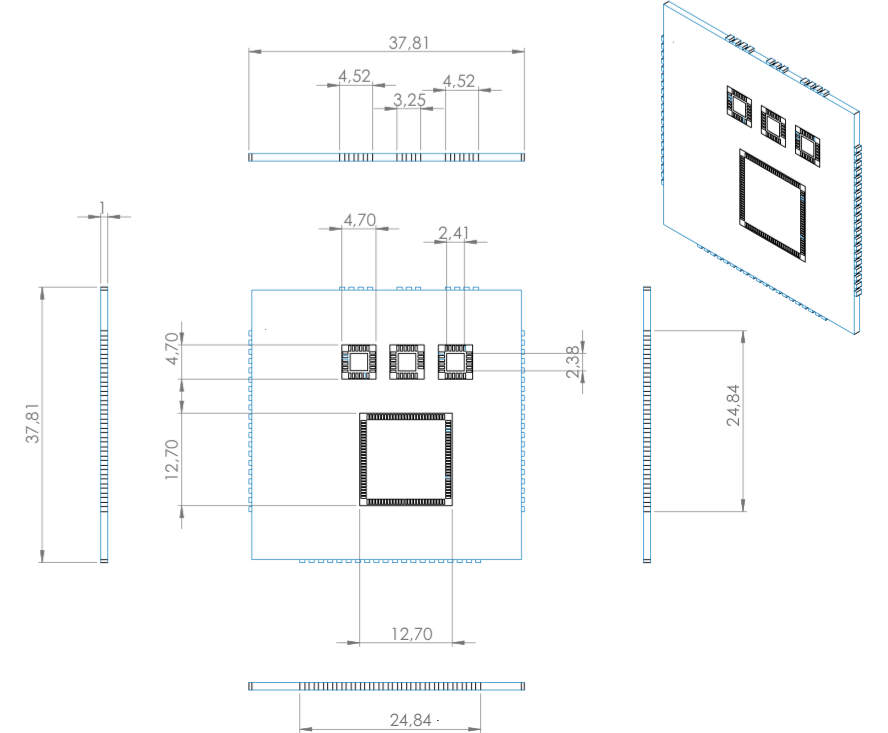 * showing 3x3 E98B LGA CoB mechanical configuration.
* showing 3x3 E98B LGA CoB mechanical configuration.